I. Clean Architecture
1. Giới thiệu:
Clean Architecture là một business architecture, nó tách rời những xử lý nghiệp vụ khỏi UI và framework. Clean Architecture phân rõ vai trò và trách nhiệm của từng layer trong kiến trúc của mình.2. Ưu nhược điểm:
Về mặt ưu điểm, Clean architecture đạt được:- Giúp logic nghiệp vụ trở nên rõ ràng.
- Không phụ thuộc vào framwork
- Các thành phần UI hoàn toàn tách biệt và độc lập.
- Không phụ thuộc vào nguồn cung cấp dữ liệu.
- Dễ dang kiểm thử.
- Clean architecture do phân tách cấu trúc thành nhiều tầng nên dẫn đến việc số lượng code sinh ra là rất lớn.
3. Các thành phần chính:
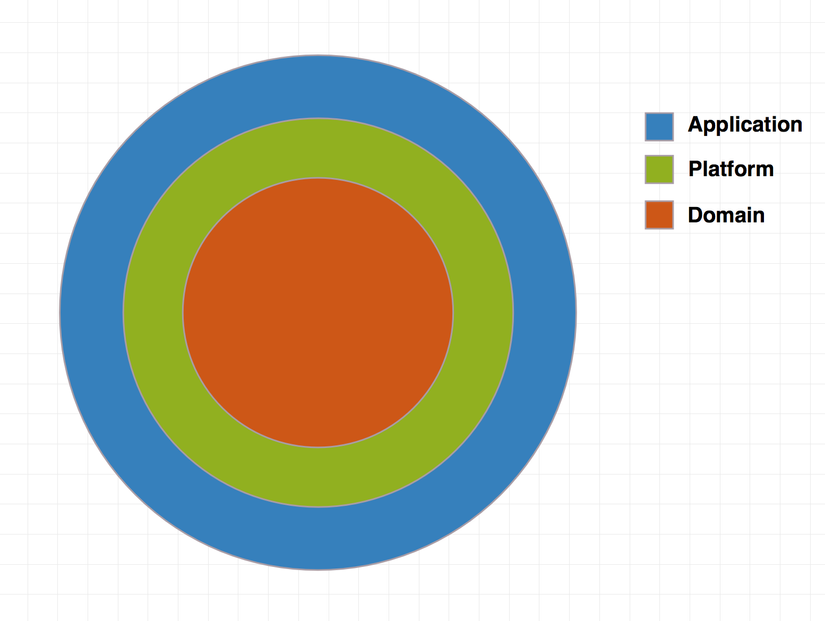
Về mặt cấu trúc, Clean architecture gồm 3 thành phần chính:
- Domain: Là tầng chứa các thành phần cơ bản của ứng dụng như các Entity, UseCase,... Tầng Domain không phụ thuộc vào bất cứ thành phần nào của UI hay bất kỳ Framwork nào và cũng không implement bất kỳ một thành phần nào của ứng dụng tại tầng này.
- Platform: Là tầng thực hiện triển khai (implement) thực hiện các phần cụ thể của tầng Domain. Tuy nhiên, tầng Platform sẽ che giấu đi những chi tiết được triển khai thực hiện.
- Application: Là tầng chịu trách nhiệm cung cấp thông tin từ ứng dụng cho user và tiếp nhận những input từ user cho ứng dụng. Nó có thể được triển khai với các mô hình như MVC, MVP, MVVM,...
II. Mô hình MVVM:
1. Giới thiệu:
MVVM là một cấu trúc ba lớp gồm 3 thành phần chính là View - View Model - Model được tạo ra với mục đích làm đơn giản hoá việc lập trình sự kiện của giao diện người dùng.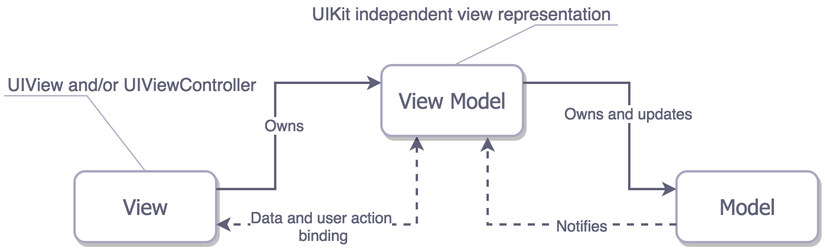
2. Các thành phần của MVVM:
- View: Giống với mô hình MVC thì View là thành phần giao diện của ứng dụng đóng vai trò hiển thị dữ liệu và tiếp nhận những tương tác từ người dùng. Tuy nhiên, khác với MVC thì View trong MVVM hoạt động tích cực hơn bởi nó có khả năng thực hiện những hành vi phản hồi lại người dùng thông qua tính năng Binding hoặc Command.
- Model: Cũng tương tự như mô hình MVC, Model là các đối tượng giúp truy xuất và thao tác với dữ liệu.
- View Model: Là lớp trung gian giữa View và Model. ViewModel đóng vai trò chung chuyển dữ liệu giữa View và Model với nhau và là nơi chứa các mã lệnh cần thiết để thực hiện Binding, Command.
3. Ưu điểm của MVVM:
MVVM mang những ưu điểm sau:- Tăng tính lỏng của code: Có thể dễ dàng thay thế View mà không ảnh hưởng tới View Model.
- Code dễ dàng được bảo trì và nâng cấp.
- Dễ dàng cho việc viết UnitTest.
4. Data Binding:
Một điều đặc biệt nữa ở trong mô hình MVVM đó là do View và Model không ràng buộc chặt với nhau mà được "bind" với nhau, nghĩa là mọi thay đổi ở Model sẽ ngay lập tức được cập nhật lên View và mọi thay đổi từ View cũng sẽ được cập nhật lại Model.Để có thể binding được dữ liệu giữa View và Model thì chúng ta cần phải sử dụng tới sự giúp đỡ của các thư viện và framework và RxSwift chính là một trong những lựa chọn tối ưu.
III. Tài liệu tham khảo:
https://github.com/sergdort/CleanArchitectureRxSwift http://blog.cleancoder.com/uncle-bob/2012/08/13/the-clean-architecture.html
Comments
Post a Comment