Nội dung
- Giới thiệu
- IBInspectable
- IBDesignable
- Kết Luận
Giới thiệu
Có thể chúng ta đã biết đến 2 thuộc tính khai báo của interface builder rất tiện lợi và sử dụng rất nhiều để tạo các custom view đó là IBInspectable và IBDesignable. Trong đó IBInspectable thể hiện properties của class trong interface builder Attribute Inspector và IBDesignable giúp cập nhật view realtime. Điều này thật tuyệt vời giúp chúng ta thiết kế, chỉnh sửa giao diện ngay trong interface builder rất nhanh mà hiệu quả.Nào chúng ta cùng tìm hiểu nhé!
Step 0: IBInspectable
Các thuộc tính IBInspectable cung cấp khả năng truy cập mới vào một tính năng cũ: Hiện tại có thể truy cập được từ thanh Attributes, các thuộc tính này đã có sẵn từ trước khi Interface Builder được tích hợp vào Xcode. của mỗi đối tượng trong một NIB, XIB hoặc Storyboard:
Dưới đây là những valid types cho IBInspectable :
Int
CGFloat
Double
String
Bool
CGPoint
CGSize
CGRect
UIColor
UIImage
Ví dụ:
class OverCustomizableView : UIView {
@IBInspectable var integer: Int = 0
@IBInspectable var float: CGFloat = 0
@IBInspectable var double: Double = 0
@IBInspectable var point: CGPoint = CGPointZero
@IBInspectable var size: CGSize = CGSizeZero
@IBInspectable var customFrame: CGRect = CGRectZero
@IBInspectable var color: UIColor = UIColor.clearColor()
@IBInspectable var string: String = "We ❤ Swift"
@IBInspectable var bool: Bool = false
}

Tất cả được thêm vào một vài thuộc tính định nghĩa người dùng trong runtime và được cài đặt giá trị khởi tạo khi View được load lên.

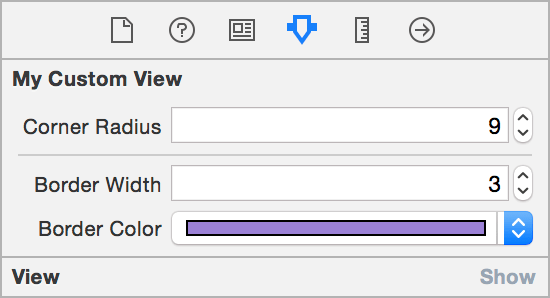
Chúng ta cùng tìm hiểu thêm ví dụ khá thông dụng về cornerRadius của UIView:
@IBInspectable var cornerRadius: CGFloat = 0 {
didSet {
layer.cornerRadius = cornerRadius
layer.masksToBounds = cornerRadius > 0
}
}
@IBInspectable var borderWidth: CGFloat = 0 {
didSet {
layer.borderWidth = borderWidth
}
}
@IBInspectable var borderColor: UIColor? {
didSet {
layer.borderColor = borderColor?.CGColor
}
}
IBDesignable
Chúng ta cùng làm quen với khái niệm khá thú vị tiếp theo là IBDesignable. Với nó, chúng ta sẽ thấy được sự thay đổi trực tiếp trên các giao diện như Xib, Storyboard. Tính năng này cho phép các tùy chình, thay đổi của bạn sẽ xuất hiện luôn mà không cần build hay run app sau mỗi lần thay đổi.Để đánh dấu một view tùy chỉnh là IBDesignable, chúng ta hãy thêm vào trước class name với prefix là @IBDesignable (hoặc macro IB_DESIGNABLE trong Objective-C):
@IBDesignable
class MyCustomView: UIView {
...
}

Khi kết hợp với thuộc tính IBInspectable, các lập trình viên có thể dễ dàng điều chỉnh việc hiển thị, tùy chỉnh các kết quả mà chúng ta muốn. Ngoài ra có một tính năng rất hay giúp chúng ta debug liên quan đến UI mà không cần phải build và chạy app đó là chúng ta vào Interface Builder, và chọn Editor ➔ Debug Selected Views.
Kết Luận
Trên đây, mình đã giới thiệu 2 thuộc tính của Interface Builder là IBInspectable / IBDesignable. Với nó, các bạn sẽ giảm tối thiểu được thời gian khi phải vật lộn với mã để thay đổi giao diện cho UIView. Hi vọng các bạn có thể áp dụng vào dự án của mình 1 cách hiệu quả.Quả thật, 2 thuộc tính của Interface Builder là IBInspectable / IBDesignable đã giúp cho việc tạo một custome class một cách dễ dàng hơn, dễ dàng thay đổi giao diện và tiết kiệm rất nhiều thời gian trong quá trình phát triển ứng dụng.
Cám ơn bạn đã dành thời gian cho bài viết này!
Comments
Post a Comment