In short, the map applies a function to each emitted element and returns its result.
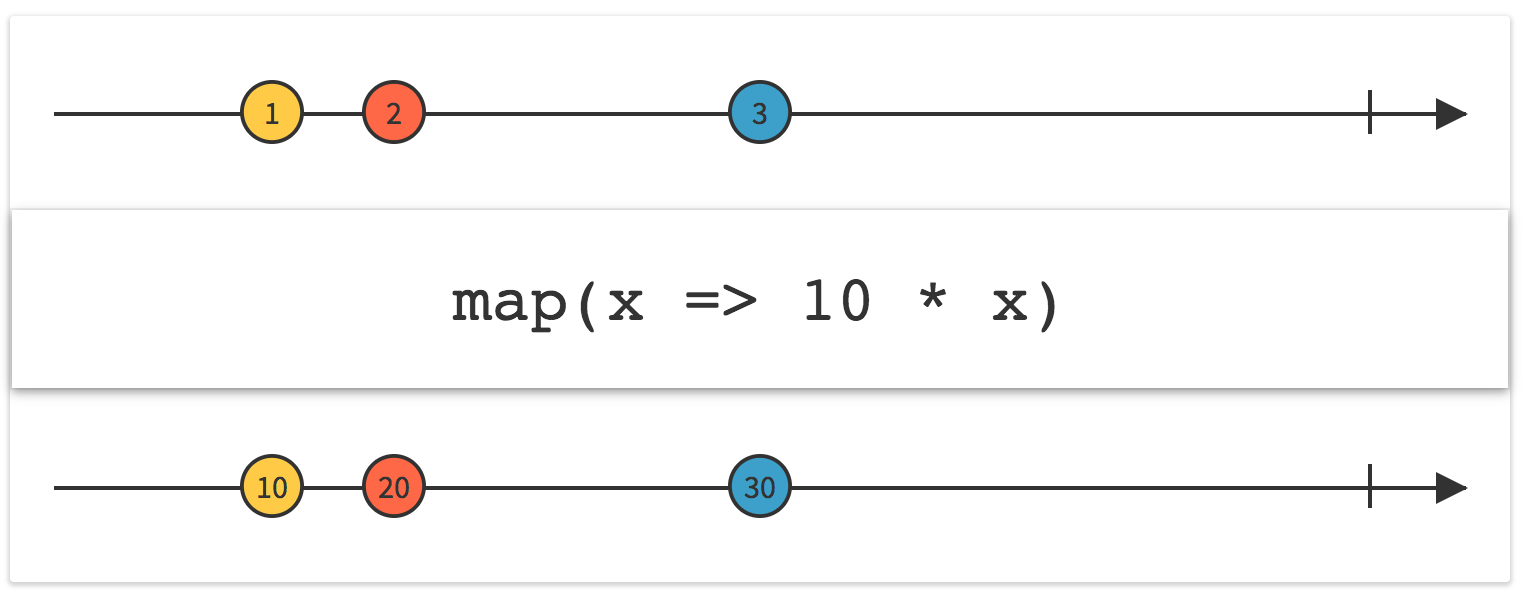
Observable<Integer> observable = Observable .just(1,2,3) .map(x -> 10 * x); observable.subscribe(System.out::println);Result: 10 20 30
So
FlatMap applies a function to each emitted element, but this function
returns the type of the Observable. I.e. 1 emitted by an element through
a flatMap to generate a set of emitted elements or not one.
Observable<String> observable = Observable
.just("A", "B", "C")
.flatMap(s -> {
System.out.println();
return Observable.just(s + "1", s + "2", s + "3");
});
observable.subscribe(s -> System.out.print(s + " "));
Result:A1 A2 A3
B1 B2 B3
C1 C2 C3
Comments
Post a Comment