Giới thiệu
Đối với lập trình viên, việc thao tác với collection là kĩ nẵng quan trọng. Trong bài viết này tôi sẽ trình bày về chức năng của các hàm xử lí với Collection trong Swift (Filter, Map, FlatMap, CompactMap, Reduce)
Filter():
Filter là một trong những hàm khá thông dụng trong Swift. Chức năng của filter là duyệt các phần tử trong mảng và trả về 1 mảng chua các phần tử thỏa mãn điều kiện cho trước.
- func filter(_ isIncluded: (Self.Element) throws -> Bool) rethrows -> [Self.Element]
Quan sát closure isInclude (self.Element) -> Bool là tham số tuyền vào, có chức năng kiểm kiểm tra phan tử có thõa mãn điều kiện để thêm lọc mảng. Nếu closure return true phần tử sẽ được thêm vào mảng và ngược lại.
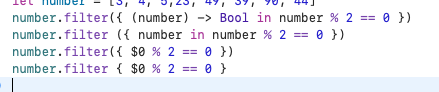
Ví dụ: Tìm các phần tử chia hết cho 2 trong mảng số nguyên.
Khi không sử sự Filter:

Ví dụ với Filter:

Rút gọn:
Map():
Map là hàm có chức năng duyệt các phần tử trong mảng và trả về mảng chữa các phần tử theo một biến đổi T.
func map<T>(_ transform: (Element) throws -> T) rethrows -> [T]
- Ví dụ:

Ví dụ duyệt mảng với map.
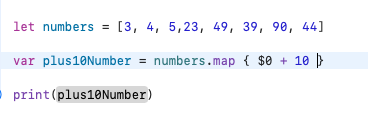
-
Trong ví dụ này hàm Map() sẽ duyệt các phần tử trong mảng và trả về mảng các phần tử theo biến đổi T.
-
Kết quả :

FlatMap():
- FlatMap tương tự như map tuy nhiên nó gộp các mảng con trong mảng trở thành 1.
ví dụ với FlatMap:
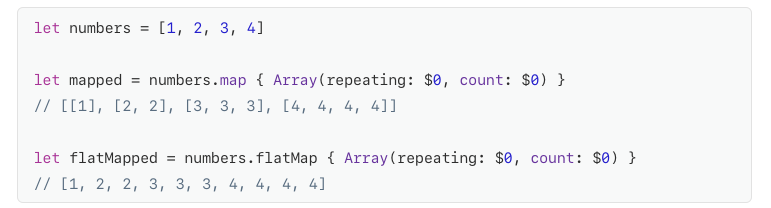
Ta có thể hiểu flatMap tương đương với cấu trúc sau trong Map.
s.flatMap(transform) == Array(s.map(transform).joined()).
Compact map():
CompactMap có chức năng tương tự như Map như giá tri trả về là một mảng không chua phần tử nil.
Xem ví dụ với Map:

Trong ví dụ với Map. các phần tử trả về sẽ chưa các phần tử không thể Convert sang Int. Và mảng trả về là Optional.

Đối với CompactMap:

Tổng kết
Trong bài viết này tôi đã trình bày các hàm duyệt và xử lí cơ bản đối với Collecttion trong swift
Comments
Post a Comment